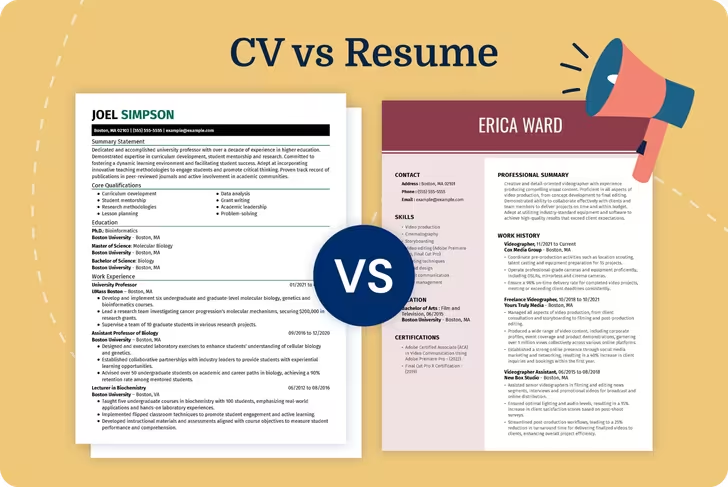
CV vs resume is one of the most frequently asked questions among job seekers, students, and professionals preparing job application documents. While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, a curriculum vitae (CV) and a resume are distinct in several important ways.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explain the differences between a CV and a resume, when to use each, what to include, and how to optimize your document for the type of job you’re applying for.
What Is a CV?
CV stands for curriculum vitae, a Latin phrase meaning “course of life.” A CV is a comprehensive, multi-page document that details your entire professional and academic history. It is most commonly used when applying for academic, research, or international positions where full credentials must be provided.
What to Include in a CV:
- Full name and contact information
- Professional summary or objective (optional)
- Education (degrees, institutions, years, honors)
- Work history (detailed descriptions of duties and achievements)
- Research experience
- Teaching experience
- Publications
- Presentations and conferences
- Awards and honors
- Grants, fellowships, or scholarships
- Certifications and licenses
- Professional affiliations
- Languages and skills
- References (optional)
A CV is typically arranged chronologically, starting with the most recent accomplishments. It may range anywhere from 2 to over 10 pages, depending on your level of experience.
What Is a Resume?
A resume is a short, targeted summary of your skills, experience, and qualifications for a specific job. It is designed to be quick to scan and tailored to match the requirements of the job posting.
What to Include in a Resume:
- Name and contact information
- Professional summary or objective
- Key skills (usually in bullet form)
- Work experience (reverse chronological order)
- Education (condensed)
- Certifications or licenses (if relevant)
- Optional sections: Volunteer experience, awards, or hobbies
A resume is usually 1–2 pages long and should be customized for every job application to highlight only the most relevant information.
Want a second opinion? Let Jerasp review your CV or Resume—for free! Just send it via WhatsApp and get expert feedback in minutes.
CV vs Resume: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | CV | Resume |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Curriculum Vitae (“course of life”) | Résumé (“summary”) |
| Length | Typically 2–10+ pages | 1–2 pages |
| Focus | Comprehensive academic and professional history | Targeted job-specific experience and skills |
| Use | Academia, research, medical, education, international jobs | Corporate, private sector, internships, general employment |
| Customization | Rarely customized | Always customized per job |
| Order | Chronological | Reverse chronological with emphasis on relevance |
| Common in | UK, EU, South Africa, academia worldwide | US, Canada, business and tech industries |
When to Use a CV vs a Resume
Understanding when to use a CV or resume depends on industry, geography, and job function.
Use a CV if:
- You are applying for academic, research, or education roles
- You are submitting a proposal for a grant, fellowship, or academic program
- The employer is based in Europe, South Africa, or parts of Asia, where “CV” is the common term
- You are working in medicine, science, or higher education
Use a Resume if:
- You are applying for a job in business, technology, retail, or most private sectors
- The position is based in North America, especially the United States or Canada
- You want to quickly show your qualifications tailored to the job description
- You are applying to startups, marketing firms, or professional services companies
Regional Differences in CV and Resume Usage
| Region | Common Term | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Resume | CV used for academic roles only |
| Canada | Resume | CV used for research/academia |
| United Kingdom | CV | Covers both CV and resume-style documents |
| Australia | CV | Often used interchangeably with resume |
| India | CV | Resume and CV often mean the same thing |
| Europe | CV | CV is the standard term for job applications |
If in doubt, always check the job posting or contact the recruiter to confirm which document is preferred.
Formatting Tips for Both CV and Resume
Tips for Formatting a CV:
- Use consistent font and spacing throughout
- Start with education, especially if applying for academic roles
- Include section headings like “Publications,” “Research,” “Teaching”
- Add page numbers if the CV is long
- Avoid irrelevant job experience
Tips for Formatting a Resume:
- Keep it short and targeted (1–2 pages)
- Focus on keywords from the job posting
- Use bullet points to describe achievements with measurable results
- Highlight skills relevant to the role
- Use clean formatting with plenty of white space
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using a resume when a CV is required (especially for academic or international jobs)
- Sending the same document to every job without tailoring it
- Exaggerating accomplishments or including outdated experience
- Neglecting formatting, making your document hard to read
- Including personal details like age, photo, or marital status (especially in resumes for US jobs)
Should You Have Both a CV and a Resume?
Yes. Ideally, every professional should keep both a CV and a resume up to date. While the CV serves as a master document of your experience, the resume is a selective, dynamic tool to be adapted for each opportunity.
Maintaining both allows you to:
- Quickly apply for jobs across different regions or industries
- Avoid rewriting your entire work history for each application
- Have a complete record of your academic and professional journey
Final Thoughts on CV vs Resume
Understanding the CV vs resume distinction is essential for presenting the right information in the right way. Submitting the correct document increases your chances of making a positive impression and landing interviews.
Use a resume when you need a concise, job-specific summary.
Use a CV when a detailed, full-history profile is expected.
Having both documents prepared ensures you’re ready for any opportunity—locally or globally.
CV vs Resume FAQs
1. Is a CV better than a resume?
Not necessarily. One is not better than the other; it depends on the job. Use a CV for academic and international roles and a resume for most corporate or industry jobs.
2. Can I use a CV to apply for a job in the US?
Only if the job is academic, medical, or research-based. For most U.S. jobs, especially in the private sector, a resume is expected.
3. Can I convert my resume into a CV?
Yes. You can expand your resume into a CV by adding sections such as publications, research, and awards. Similarly, you can condense a CV into a resume by focusing only on the most relevant information.
4. What if I don’t know whether to submit a CV or a resume?
If the job posting isn’t clear, contact the recruiter or HR department. As a general rule: use a resume for business jobs and a CV for academic or international jobs.
5. Are there templates for both documents?
Yes. You can find many professional resume and CV templates online that meet industry standards. Choose one that matches the style and formality of the job you’re applying to.